In this article, I am going to demonstrate the following:
- How to insert the output of a table-valued function in a SQL table.
- How to insert the output of a table-valued function which is created on the remote database server.
What is “Insert into” statement
In RDBMS, “Insert into” is one of the basic SQL statements. It is used to insert new records in a SQL table. Using the statement, we can perform the following tasks:
- Insert new records in a table (Basic Insert).
- Insert values of a specific column in a table.
- Insert the output generated by a stored procedure in a SQL table.
To demonstrate the above, let’s create a table named “Students” on DemoDatabase. Execute the following code to create the table:
CREATE TABLE STUDENTS
(
ID INT IDENTITY(1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
FIRSTNAME VARCHAR(250),
LASTNAME VARCHAR(250),
ADMISSIONDATE DATETIME,
GRADE CHAR(1)
)
Perform basic insert
To perform basic insert, we need to provide the name of the target table and values of the table. The following is a basic syntax of the basic insert statement:
INSERT INTO <target TABLE NAME> VALUES ( <value FOR COLUMN 1 >, <value FOR COLUMN 1 >.. )
For example, we want to insert first name, last name, and grade of three students in the “Students” table. To do that, execute the following code:
INSERT INTO STUDENTS
VALUES ('NISARG',
'UPADHYAY',
'2018-09-11',
'A'),
('RAGHAV',
'DATTA',
'2017-10-01',
'A'),
('KIRAN',
'AMIN',
'2016-01-31',
'A')
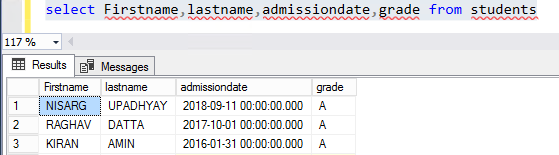
Execute the “Select” query against“Student” to review the results.
SELECT FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, ADMISSIONDATE, GRADE FROM STUDENTS
The result is as follows:
Insert values of a specific column in the table
To insert values in specific columns of a table, you need to provide the name of the target table and name of the columns in which you want to insert data. The following is the syntax.
INSERT INTO <TARGET TABLE NAME> ( COLUMN 1 , COLUMN 2 ) VALUES ( <VALUE FOR COLUMN 1 >, <VALUE FOR COLUMN 1 >.. )
For example, we want to insert first name and last name of two students in the “Students” table. To do that, execute the following code:
INSERT INTO STUDENTS
(FIRSTNAME,
LASTNAME)
VALUES ('NIMESH',
'UPADHYAY'),
('RUPESH',
'DATTA')
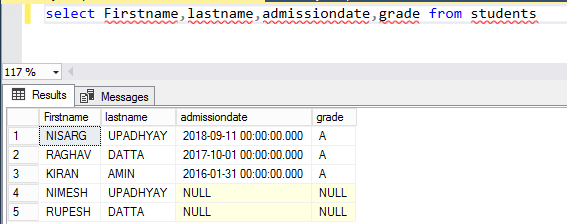
Execute the “Select” query against the “Students” table.
SELECT FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, ADMISSIONDATE, GRADE FROM STUDENTS
The output looks as follows:
Insert the output, generate by a stored procedure
To insert the output of a stored procedure in the table, we need to specify the target table name and the source stored procedure. To generate the output of the stored procedure, we need to use the “exec” or “EXECUTE” keyword. So, we need to provide the table name or names of the columns followed by the “exec” keyword. The following is the syntax:
INSERT INTO <TARGET TABLE NAME> ( COLUMN 1 , COLUMN 2 ) EXEC <PROCEDURENAME>
For example, we want to insert the output of the procedure which populates the names of the students whose admission date is not null. To do that, we will create a stored procedure named “spGet_Student_AdmissionDate”. To create a stored procedure, execute the following code:
USE DEMODATABASE GO CREATE PROCEDURE SPGET_STUDENT_ADMISSIONDATE AS BEGIN SELECT ISNULL(FIRSTNAME, '') + ' ' + ISNULL(LASTNAME, '') AS STUDENTNAME, ADMISSIONDATE, GRADE FROM STUDENTS WHERE ADMISSIONDATE IS NOT NULL END
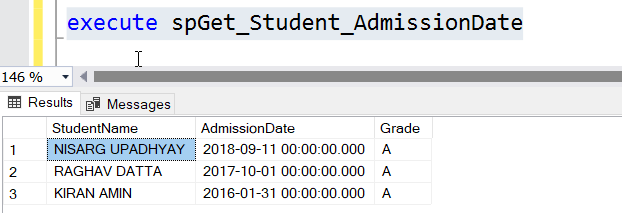
Once the procedure is created, run the procedure by executing the following code:
EXECUTE spGet_Student_Admissiondate
The output looks as follows:
As I mentioned above, we want to insert the output of the stored procedure named “spGet_Student_Admissiondate” in a temporary table. Firstly, execute the following code to create the table:
( ID INT IDENTITY(1, 1), STUDENTNAME VARCHAR(250), ADMISSIONDATE DATETIME, GRADE CHAR(1) )
Once the table is created, execute the following code to insert the output of “spGet_Student_Admissiondate” to “#TempStudents”.
INSERT INTO #TEMPSTUDENTS EXECUTE SPGET_STUDENT_ADMISSIONDATE Output: (3 rows affected)
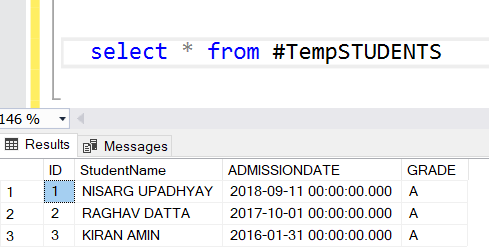
Now let’s check the output of “#TEMPSTUDENTS”. To do that, execute the following code:
Now, as I mentioned above, I am going to demonstrate how can we insert an output generated by a table-valued function in a SQL Table. Firstly, let’s understand what is a table-valued function.
What is Table-Valued Function
A table-valued function is a special T-SQL code that accepts parameter/parameters and based on the conditions defined in a variable, returns the result set in the table variable. The following are the benefits of using the table-valued function:
- It can be executed within the Select query.
- It can be used in multiple parts of a query, e.g.g in the Case statement, where/having clauses.
- The output of a table-valued function is a recordset, hence you can join the function with tables.
Insert Output of inline table-valued function in SQL table
In this section, I am going to explain how to insert the output of a table-valued function in a SQL table using T-SQL.
For demonstration, I am using the AdventureWorks2014 database. I created an inline multi-valued table function named “GetEmployeesbyHireDate.” This function populates information of employees, hired within a specific date and time. The function uses the @FormDate and @Todate parameters to filter the data. The output of the function will be stored in a SQL Table.
The following code creates a function:
CREATE FUNCTION GETEMPLOYEESBYHIREDATE (@FROMDATE AS DATETIME, @TODATE AS DATETIME) RETURNS @EMPLOYEES TABLE ( EMPLOYEENAME VARCHAR (MAX), BIRTHDATE DATETIME, JOBTITLE VARCHAR(150), EMAILID VARCHAR(100), PHONENUMBER VARCHAR(20), HIREDATE DATETIME ) AS BEGIN INSERT INTO @EMPLOYEES SELECT ( ISNULL( B.FIRSTNAME, '') + ' ' + ISNULL( B.MIDDLENAME, '') + ' ' + ISNULL( B.LASTNAME, '') )AS EMPLOYEENAME, A.BIRTHDATE, B.JOBTITLE, B.EMAILADDRESS, B.PHONENUMBER, A.HIREDATE FROM [HUMANRESOURCES].[EMPLOYEE] A INNER JOIN [HUMANRESOURCES].[VEMPLOYEE] B ON A.BUSINESSENTITYID = B.BUSINESSENTITYID WHERE A.HIREDATE BETWEEN @FROMDATE AND @TODATE RETURN END
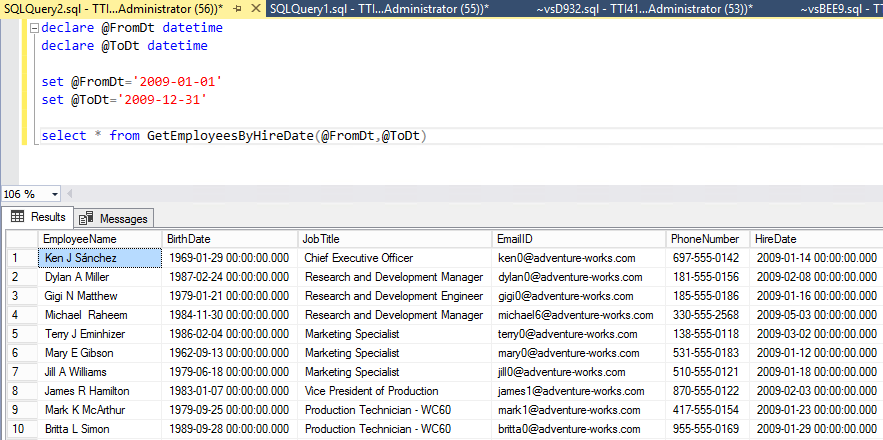
Using the Select query, we can get the output of a SQL Function. For example, you want to populate a list of employees, recruited within the year 2009. Execute the following query to get the list:
DECLARE @FROMDT DATETIME DECLARE @TODT DATETIME SET @FROMDT='2009-01-01' SET @TODT='2009-12-31' SELECT * FROM GETEMPLOYEESBYHIREDATE(@FROMDT, @TODT)
The output of the above query looks as follows:
Now, create a table named “tblEmployee” to store the output of the “GetEmployeesbyHiredate” function. The following code creates the table named “tblEmployee”.
CREATE TABLE TBLEMPLOYEES ( EMPLOYEENAME VARCHAR (MAX), BIRTHDATE DATETIME, JOBTITLE VARCHAR(150), EMAILID VARCHAR(100), PHONENUMBER VARCHAR(20), HIREDATE DATETIME )
As I mentioned earlier, we want to populate the information of the employees, who were hired in 2009. To do that, insert the output of the GetEmployeesbyHireDate function in the tblEmployees table. To do that, execute the following code:
DECLARE @FROMDT DATETIME DECLARE @TODT DATETIME SET @FROMDT='2009-01-01' SET @TODT='2009-12-31' INSERT INTO TBLEMPLOYEES SELECT EMPLOYEENAME, BIRTHDATE, JOBTITLE, EMAILID, PHONENUMBER, HIREDATE FROM GETEMPLOYEESBYHIREDATE(@FROMDT, @TODT)
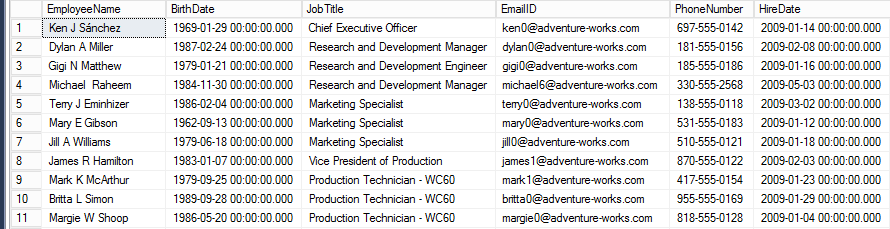
Let’s verify that data has been inserted in the table. To do that, execute the following code:
SELECT * FROM TBLEMPLOYEES
The output looks as follows:
Insert data in tables from Remote databases
Sometimes, you may want to extract data from the servers stored in a different data center. This can be done using SQL Linked server.
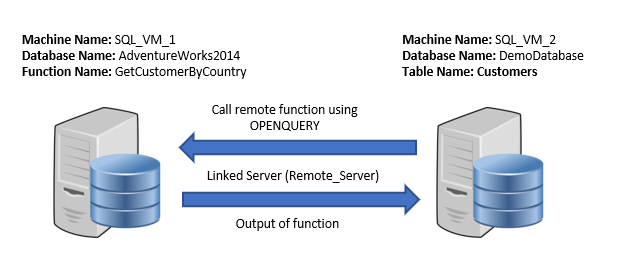
In this section, I will explain how to insert the output of the table valued function, created on the remote server. Now to demonstrate the scenario, the following is the setup.
[table id=57 /]
In the demo, we will perform the following tasks:
- On the source server (SQL_VM_1), create a table-valued function named “getCustomerByCountry” on the “AdventureWorks2014” database to populate the data.
- On the destination server, create a linked server named “Remote_Server” to execute the function (getCustomerByCountry).
- On the destination server, create a table, named “Customer” to store data, retrieved by the remote function (getCustomerByCountry).
The following image illustrates the setup.
The task to be performed on a Source server:
On the source server (SQL_VM_1), create a function named “getCustomerByCountry.” It populates details of a customer located in a specific country or region. The function uses the @CountryName parameter to filter the data. Execute the following code to create the function.
Alter FUNCTION Getcustomerbycountry(@CountryName VARCHAR)
returns @Customers TABLE (
customer_name VARCHAR(500),
phoennumber VARCHAR(50),
emailaddress VARCHAR(100),
address VARCHAR(max),
city VARCHAR(150),
country VARCHAR(250),
postalcode VARCHAR(50))
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO @Customers
SELECT customer_name,
phoennumber,
emailaddress,
address,
city,
country,
postalcode
FROM customers
WHERE country =@CountryName
RETURN
END
The tasks to be performed on Destination Server:
To populate data from the source server (SQL_VM_1), first, create a linked server between the source (SQL_VM_1) and destination (SQL_VM_2). Execute the following code on the destination server (SQL_VM_2) to create a linked server.
USE [MASTER] GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_ADDLINKEDSERVER @SERVER = N'SQL_VM_1', @SRVPRODUCT=N'SQL SERVER' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_ADDLINKEDSRVLOGIN @RMTSRVNAME=N' Remote_Server',@USESELF=N'FALSE',@LOCALLOGIN=NULL,@RMTUSER=N'SA',@RMTPASSWORD='########' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'COLLATION COMPATIBLE', @OPTVALUE=N'TRUE' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'DATA ACCESS', @OPTVALUE=N'TRUE' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'DIST', @OPTVALUE=N'FALSE' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'PUB', @OPTVALUE=N'FALSE' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'RPC', @OPTVALUE=N'TRUE' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'RPC OUT', @OPTVALUE=N'TRUE' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'SUB', @OPTVALUE=N'FALSE' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'CONNECT TIMEOUT', @OPTVALUE=N'0' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'COLLATION NAME', @OPTVALUE=NULL GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'LAZY SCHEMA VALIDATION', @OPTVALUE=N'FALSE' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'QUERY TIMEOUT', @OPTVALUE=N'0' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'USE REMOTE COLLATION', @OPTVALUE=N'TRUE' GO EXEC MASTER.DBO.SP_SERVEROPTION @SERVER=N'Remote_Server', @OPTNAME=N'REMOTE PROC TRANSACTION PROMOTION', @OPTVALUE=N'FALSE' GO
Once the linked server is created, create a SQL table to store the information of customers, and populate it by executing the SQL function, created on the source server (SQL_VM_1).
Execute the following code to create a table.
USE DEMODATABASE
GO
CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS
(
ID INT IDENTITY(1, 1),
CUSTOMER_NAME VARCHAR(500),
PHONENUMBER VARCHAR(50),
EMAILADDRESS VARCHAR(100),
ADDRESS VARCHAR(MAX),
CITY VARCHAR(150),
COUNTRY VARCHAR(250),
POSTALCODE VARCHAR(50)
)
Using a linked server, we can execute the table-valued function created on a remote database server. When you try to execute the function using Linked server, the following error occurs:
Msg 4122, Level 16, State 1, Line 28 Remote table-valued function calls are not allowed.
Hence to execute any function on the remote server, we need to use the OPENQUERY keyword. It is used to initialize the ad hoc distributed query using a linked server. Refer this article to understand the concept of OPENQUERY.
To use OPENQUERY, we need to enable advanced configuration parameter named “Ad Hoc Distributed Queries” on the source and destination servers. Execute the following code to enable it.
USE MASTER GO EXEC SP_CONFIGURE 'SHOW ADVANCED OPTION', 1 RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE EXEC SP_CONFIGURE 'AD HOC DISTRIBUTED QUERIES', 1 RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE
Now I want to populate the list of customers, located in the United Kingdom and insert them in the “Customers” table. As I mentioned, the function accepts country name to filter the records. Now, we need to execute the following script on the Destination server (SQL_VM_2) to populate the list of customers located in “United Kingdom”.
SELECT CUSTOMER_NAME,
PHOENNUMBER,
EMAILADDRESS,
ADDRESS,
CITY,
COUNTRY,
POSTALCODE
FROM OPENQUERY([TTI609-VM2],
'DECLARE @COUNTRY VARCHAR(150)
SET @COUNTRY=''UNITED KINGDOM''
SELECT * FROM [ADVENTUREWORKS2014].DBO.GETCUSTOMERBYCOUNTRY(''''+ @COUNTRY +'''')'
)
The output looks as follows:
Now, to insert data populated by in “Customers” table, execute the following script on the destination server (SQL_VM_2).
INSERT INTO CUSTOMERS (CUSTOMER_NAME,PHONENUMBER,EMAILADDRESS,ADDRESS,CITY,COUNTRY,POSTALCODE)
SELECT CUSTOMER_NAME,
PHOENNUMBER,
EMAILADDRESS,
ADDRESS,
CITY,
COUNTRY,
POSTALCODE
FROM OPENQUERY([TTI609-VM2],
'DECLARE @COUNTRY VARCHAR(150)
SET @COUNTRY=''UNITED KINGDOM''
SELECT * FROM [ADVENTUREWORKS2014].DBO.GETCUSTOMERBYCOUNTRY(''''+ @COUNTRY +'''')'
)
/*Output*/
(1913 rows affected)
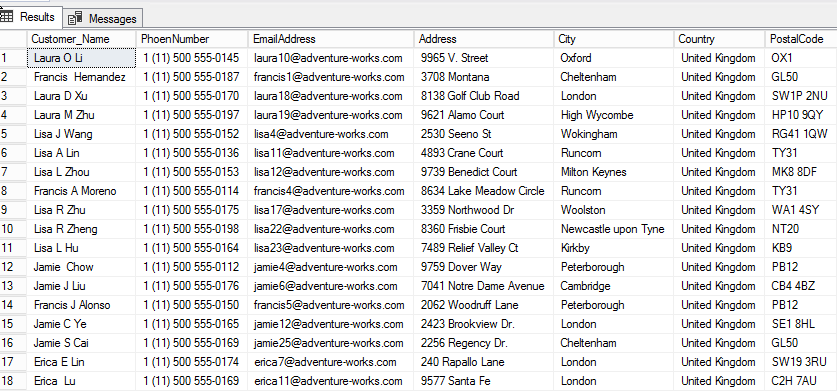
Now let’s verify whether data has been inserted properly. To check, execute the following query on the Destination server (SQL_VM_2).
USE DEMODATABASE
GO
SELECT TOP 20 CUSTOMER_NAME,
PHONENUMBER,
EMAILADDRESS,
ADDRESS,
CITY,
COUNTRY,
POSTALCODE
FROM CUSTOMERS
The output looks as follows:
Summary
In this article I have covered:
- “Insert Into” statement and its usage.
- How to save the output of the table-valued function in a SQL table.
- How to save the output of the table-valued function to the SQL table located on remote server using Linked Server.