INTRODUCTION
SQL Server is designed to allow multiple databases on a single instance. With this model it is possible to have databases sitting on an instance which are not the same version as the instance itself. You can think of this as running the database in the “backward compatibility mode.” To break it down further, we are saying that you can have a 2008 database deployed on an SQL Server 2016 instance. In such a scenario, the database is, for instance, allowed to use certain constructs that belong to a previous version of SQL Server.

There are cases where you would like to upgrade all databases in your instance to a more recent version for security reasons or to align with your organization’s policies. When doing this it may not be safe to assume that such a database will automatically work when upgraded. Using Upgrade Advisor, you can determine whether your existing databases are suitable for upgrade to SQL Server 2016 or any other higher version.
PREREQUISITES
Download Upgrade Advisor 2016 from Microsoft’s website. In this article, we have focused on Upgrade Advisor 2016; however, the latest version of Upgrade Advisor is called Data Migration Assistant and can be downloaded here. Once downloaded, you can install Upgrade Advisor 2016 on the computer that you will execute the analysis from. Note that this need not be the computer where SQL Server is installed.
PROCEDURE
1. Launch Upgrade Advisor and select the option to ANALYZE AND MIGRATE TO SQL SERVER
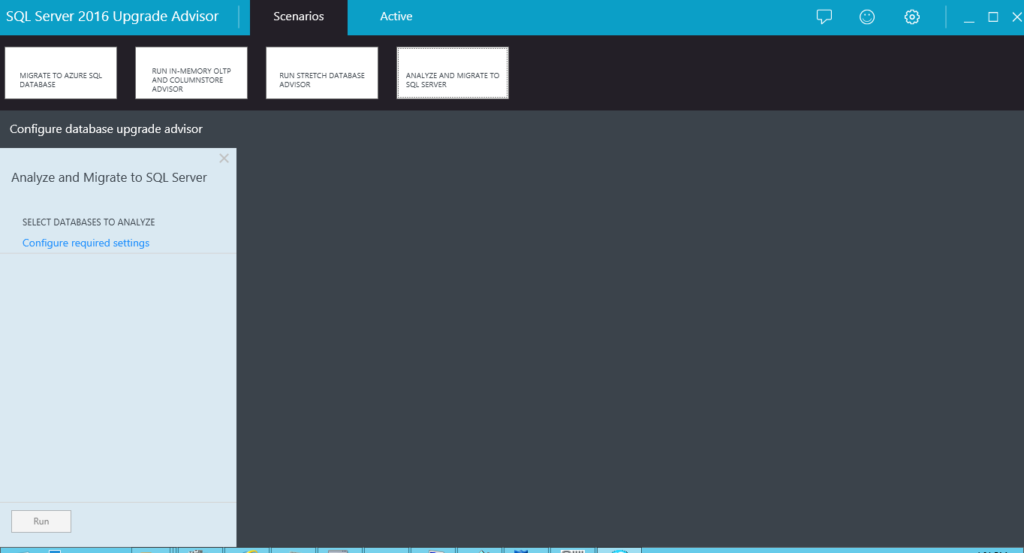
Figure 1 shows the splash screen that is displayed when you launch Upgrade Advisor. We see that the advisor offers four options for the analysis:
- Migrate to Azure SQL Database
- Run in-memory OLTP and ColumnStore advisor
- Run stretch database advisor
- Analyze and Migrate to SQL Server
The tool offers the database administrator an opportunity to properly prepare for any of these listed steps. It is better to predict what might happen if you embark on any of the listed tasks than to simply attempt them, fail and then realize why.
In the current scenario, we are focusing on number (4) which is Analyze and Migrate to SQL Server. We want to know whether existing databases can be migrated to SQL Server 2016, what we may need to do before embarking on such a migration, and what we may need to do as additional steps after the migration.
We select the option Analyze and Migrate to SQL Server and then click the Run button.
2. Connect to the desired instance
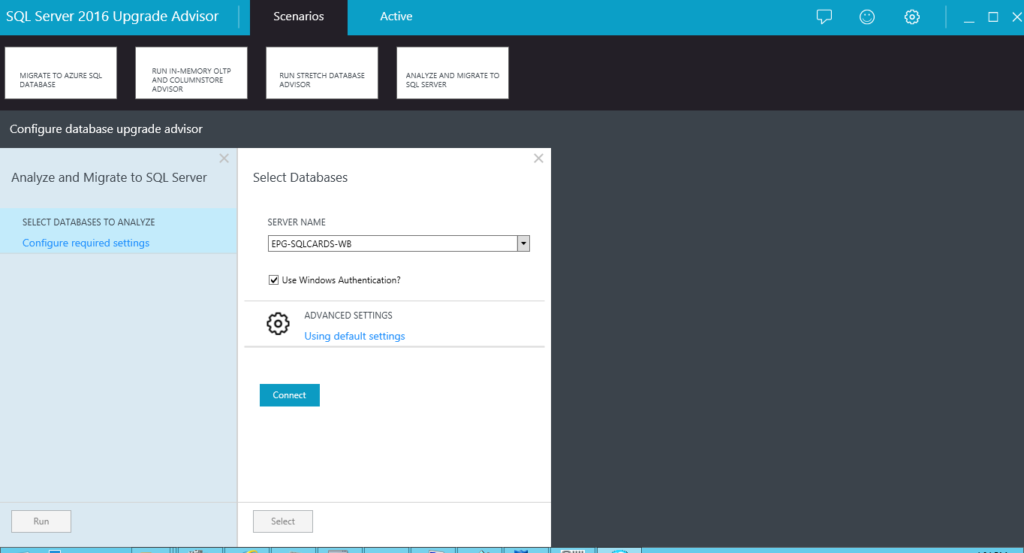
We must then connect to the instance we wish to analyze (Figure 2) and select the databases we want to analyze (See Figure 3). Type the instance name in the field shown and click Connect. In this scenario, we are running Upgrade Advisor on the same server where our SQL Server instance is hosted, so the tool can enumerate the installed instances and allow us to select from a menu. Recall that this behavior for tools that connect to SQL Server instance is made possible by SQL Server Browser.
3. Select the desired database(s)
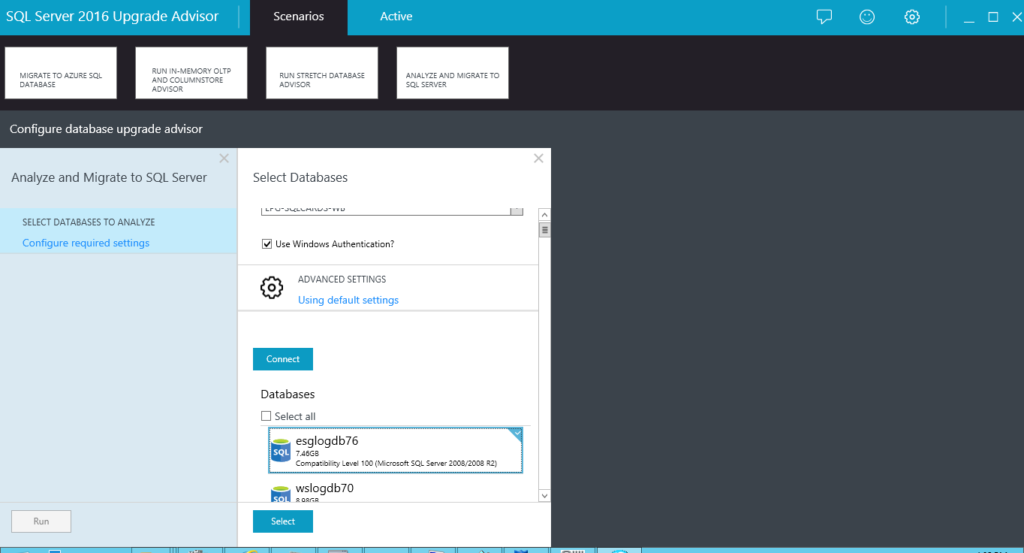
We select the desired database(s) (See Figure 3) and click the Select button. Once the database is selected (See Figure 4), click Run.
4. Run the analyzer

5. Analysis is complete
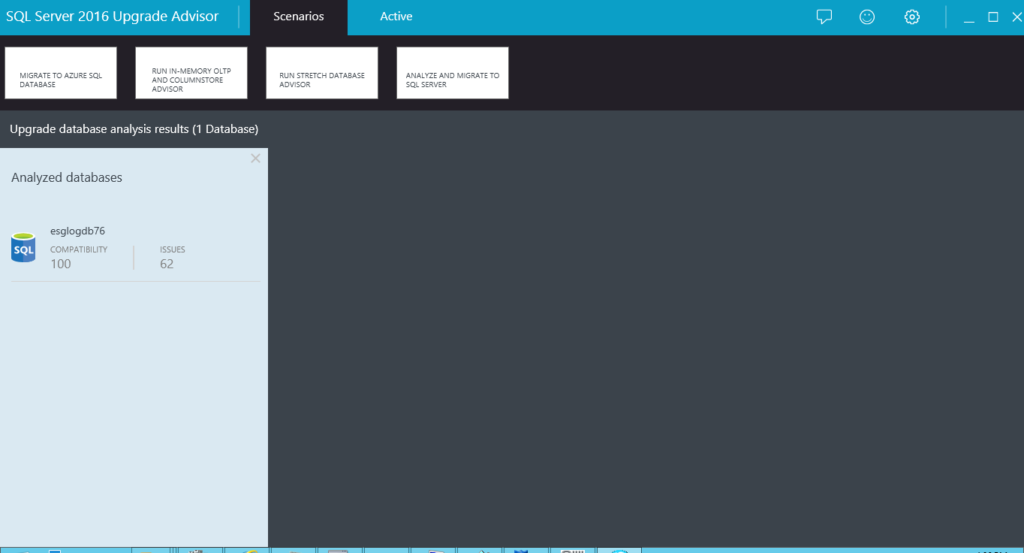
The Advisor analyzes the database(s) selected and returns any issues of concern about the database that may hinder the upgrade or pose a problem in future if you do proceed with the upgrade. Click Issues to see the analysis results (Figure 6).
6. Review the results and export the report
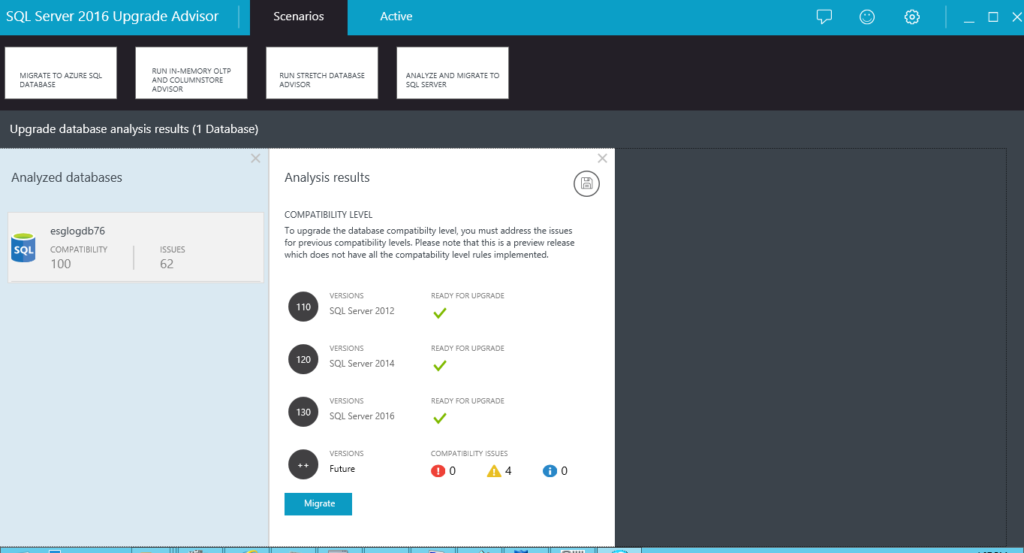
The results show us that we can safely upgrade to SQL Server 2016 but warns us about compatibility issues with earlier releases and future releases (beyond SQL Server 2016) which need to be addressed. You do realize that the future versions being spoken of here are current versions at the time of this article such as SQL Server 2017 and SQL Server 2019. At this point, we can choose to migrate to SQL Server 2016, and we can also choose to save the results and review them in greater detail. We click the Save icon highlighted in orange.
7. Choose your preferred file type and click EXPORT
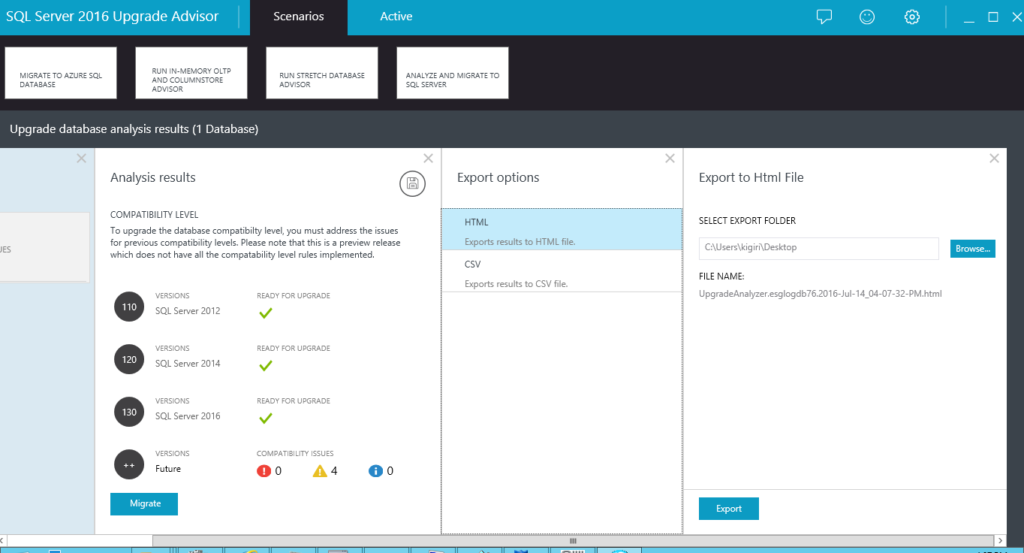
Upgrade Advisor 2016 allows us to save the output either as HTML or CSV in a path we choose. Once the file is downloaded, we can review it.
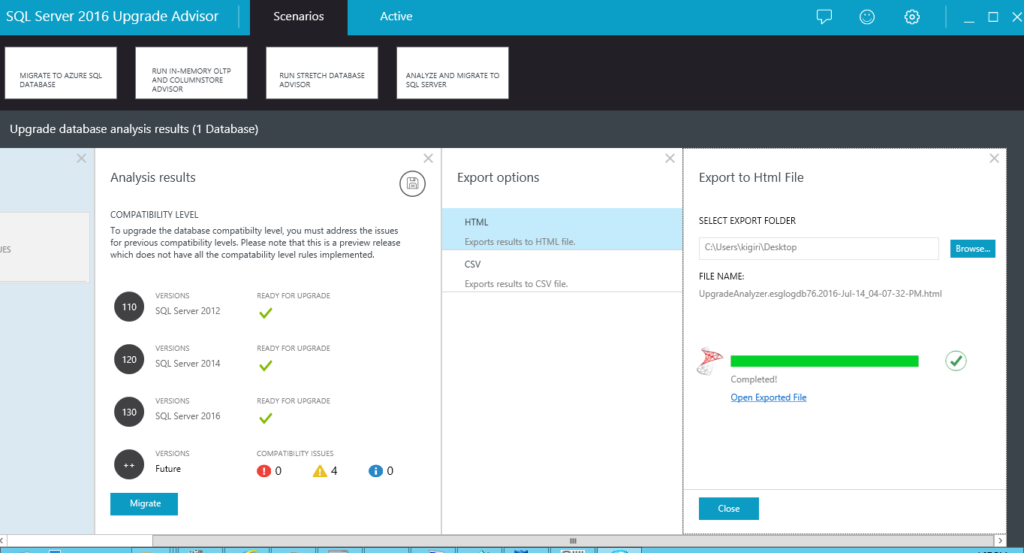
8. Open the Exported File
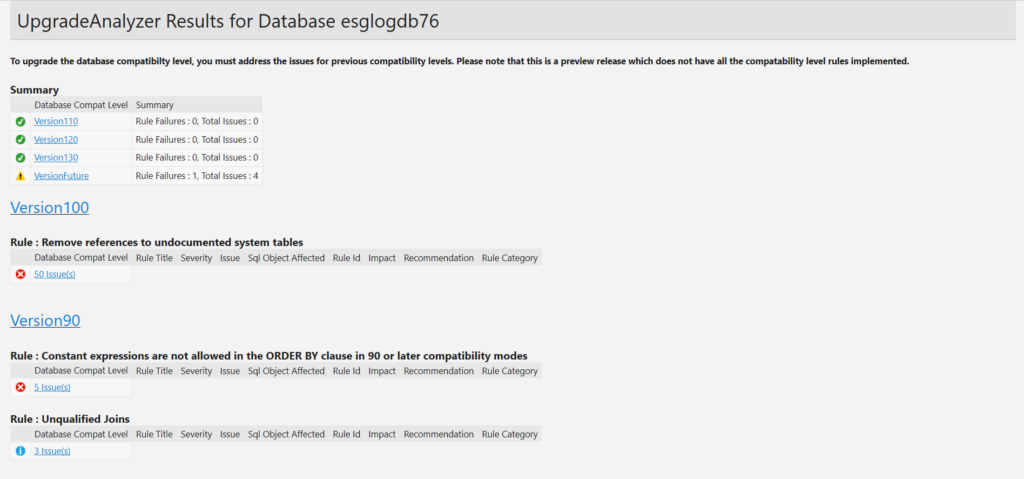
The summary page looks like what is shown in Figure 9. We can drill down in the report by clicking the hyperlinks to view the more details of the issues. Notice that there are issues highlighted about previous releases which are yet to be addressed. These issues border on code used on the stored procedures in the database we are analyzing. The database was written for an older version of SQL Server thus still references old system tables (See Figure 10).
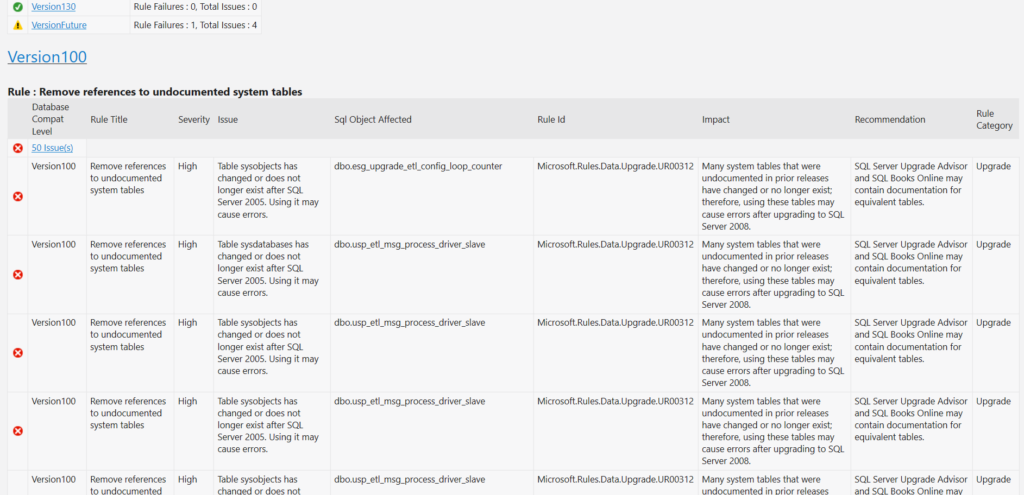
Conclusion
SQL Server allows you to operate a database at a lower compatibility level than that of the instance. At some point, however, you may need to upgrade the database. When embarking on such a venture, it pays off to do some analysis. We have examined Upgrade Advisor 2016 in this article which gives us a means of doing this analysis. A more recent version of this tool is called Data Migration Assistant and is available for download on the Microsoft website.
References
Download Data Migration Assistant
Tags: sql server, sql server 2016, sql upgrade advisor Last modified: September 20, 2021







