SQL Server Agent is a component used for the database tasks automation. For instance, we need to perform Index maintenance on Production servers during the non-business hours only. So, we create a SQL Server job of running index maintenance and schedule it for “off” hours.
When we install SQL Server, the SQL Server Agent service is disabled. First, we enable it and start it manually. Then, we configure the SQL Server job, using SQL Server Management Studio and the system stored procedures of the MSDB database.
This article explains how to create a SQL Server Job using the system stored procedures of the MSDB database.
The system stored procedures of the MSDB database
SQL Server uses the following ones:
- sp_add_job: the procedure is for creating a new job. If it is successful, it returns @job_id. The following arguments are applicable:
- @job_name: It is a unique job name.
- @enabled: Job is enabled or disabled. Once a job is created, you can set the parameter’s value as 1 to enable the job.
- @notify_level_eventlog: This parameter is used for writing the status of the SQL Job in Windows event viewer.
| Value | Description |
| 0 | The outcome of the job will not be written to the event log. |
| 1 | If the job executes successfully, the outcome will be written to the event viewer |
| 2 (default value) | If the job fails, the outcome and error message will be written to the event viewer |
| 3 | The outcome of the job is written to the event viewer. |
- @notify_level_email: This parameter serves to send the email about the SQL Job outcome. The valid values of the parameter are the same as the @notify_level_eventlog argument values.
- @notify_level_page: This parameter serves to send the pager notification of the SQL Job outcome. The valid values of the parameters are the same as the @notify_level_eventlog argument values.
- @delete_level: This parameter serves to delete the job after completion. In this case, the value of the parameter should be 1. Note that the default value is 0; then, it won’t delete the job after completion.
- @category_level: This parameter indicates the job category values. The default value is NULL.
- @owner_login_name: The value is the domain name or the job owner’s SQL Login name.
2. Sp_add_jobserver: This stored procedure serves to specify the target server for the SQL Job execution. The procedure accepts the following arguments:
- @job_id: It is a UNIQUEIDENTIFIER of the SQL Job. The default value of this argument is NULL.
- @job_name: It is the name of the SQL Job.
- @server_name: It is the name of the server where you want to run the SQL Job. The default argument value can be the local server (LOCAL) or the target server hostname.
3. sp_add_jobstep: This stored procedure works for adding the job step in SQL Job. The procedure uses the following arguments:
- @job_name: The name of the job in which you are adding the step. It is an SYSNAME with NULL as the default value.
- @step_name: The name of the step. It is an SYSNAME with NULL as the default value.
- @step_id: The sequential ID of the job step. It is an incremental number without a gap. It is an INT value, and the default value is NULL.
- @cmdexec_success_code: This value is returned by the CmdExec subsystem. It indicates whether the command execution was successful. The code is int value with 0 as a default value.
- @on_sucess_action: This value indicates the action that should be performed after the job step completes successfully. The values can be any of the following:
| Value | Description |
| 1 | Quit the job and return success |
| 2 | Quit the job and return failed |
| 3 | Go to the next job step |
| 4 | Go to the step id of on_success_step_id |
- @on_fail_action: specify what action to perform if the job steps fail. It is an INT value, and the default value is NULL.
- @retry_attempt: specify the number of retry attempts after the job step failure. It is an INT value, and the default value is NULL.
- @retry_interval: set the time interval (minutes) between two SQL Job step failure attempts. It is an INT value, and the default value is NULL.
- @os_run_priority:
- @Subsystem: specify the name of the subsystem used by SQL Server Agent to execute the command. The valid values are the following:
| Subsystem value | Description |
| CmdExec | Operating system command or the executable file(*.exe,*.bat) |
| ANALYSISQUERY | SQL Server analysis service queries, for example, MDX, DMX. |
| ANALYSISQUERY | SQL Server analysis service command, for example, XMLA. |
| SSIS | SQL Server integration service package. |
| PowerShell | PowerShell command or script. |
| T-SQL | T-SQL Query or Stored procedure |
| Distribution | SQL Server replication distributor agent. |
| Snapshot | SQL Server replication snapshot agent. |
| LogReader | SQL Server replication Log reader agent. |
| Queuereader | SQL Server replication queue reader. |
- @command: specify the command that the SQL Server Agent Service should execute through the subsystem. The data type is varchar(max), and the default value is NULL.
- @Database_name: Specify the name of the database where you want to run the command. This parameter is useful when you are running a T-SQL script using SQL Server Agent.
4. Sp_add_jobschedule: the stored procedure serves to create the SQL Job schedule. This procedure uses the following arguments:
- @job_name: specify the name of the SQL Job. The schedule will be made for the SQL job specified in the @job_name argument.
- @name: the name of the schedule. The data type is varchar, and the default value is NULL.
- @enabled: set 1 to enable the schedule or 0 to disable the schedule.
- @freq_type: indicates the time of the SQL job execution. The data type of the parameter is INT, and the default value is 0. The valid values are any of the following:
| Value | Description |
| 1 | The job will be executed only One time. |
| 4 | Daily. |
| 8 | Weekly |
| 16 | Monthly |
| 64 | Execute the job when the SQL Server Agent Service starts |
| 128 | Execute the SQL job when the server is idle. |
- @freq_interval: indicates the day of the SQL job execution. The data type is INT, and the default value is 0. The value depends on the value specified in the @freq_type parameter. The valid values are any of the following:
| Value | Effect on the Job schedule |
| 1 (Once) | The @Freq_interval will not be used. |
| 4 (Daily) | Every @freq_interval days |
| 8 | The value of the @Freq_interval can be any of the following: 1 = Sunday 2 = Monday 4 = Tuesday 8 = Wednesday 16 = Thursday 32 = Friday 64 = Saturday |
| 16 | Run the job on the @Freq_interval day of the month |
| 64 | The @Freq_interval will not be used |
| 128 | The @Freq_interval will not be used |
- @freq_subday_type: specify the unit of the freq_subday_interval. The data type is INT, and the default value is NULL.
- @active_start_date: set the date when you want to start the job execution. The data type is INT, and it does not have a default value. The date format is YYYYMMDD. The value must be greater or equal than 19900101.
- @active_end_date: specify the date when to stop the job execution. The data type is INT, with no default value. The date format is YYYYMMDD, and the value must be greater or equal than 19900101.
- @active_start_time: specify the time when you want to start the job execution. The data type is INT, without a default value. The time format is HHMMSS.
- @active_end_time: specify the time when you want to stop the job execution. The data type is INT, without a default value. The time format is HHMMSS.
T-SQL Code to create a SQL Job
To illustrate the processes, we use the SQL Server 2019 on the workstation with the AdventureWorks2017 database, restored from a backup. We create a SQL Job named Daily Full Backup – it generates a backup of the AdventureWorks2017 database and copies it on C:\Backups location.
First, we must enable the Agent XPs. It is an advanced option. Therefore, we first enable the advanced configuration option and the Agent XPs component.
To do that, run the following query:
EXEC Sp_configure
'Show advanced options',
1
go
RECONFIGURE WITH override
EXEC Sp_configure
'Agent XPs',
1
go
RECONFIGURE WITH override Once the Agent is enabled, we start the Agent service.
Open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to the SQL Server instance. Then, right-click on SQL Server Agent and click Start.
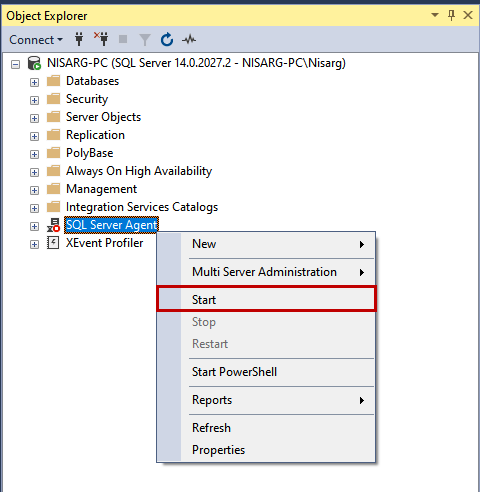
After the start of the Agent, we can create the SQL Server agent jobs.
As mentioned, we will create a SQL job to generate a backup of AdventureWorks2017 database. For this, we run the following command using SQL Server Agent.
N'Backup Database [AdventureWorks2017] to disk=''C:\Backups\AdventureWorks2017.bak'' with compression'To create a new SQL Job named Daily Full Backup, execute the following script:
USE [msdb]
go
DECLARE @jobId BINARY(16)
EXEC msdb.dbo.Sp_add_job
@job_name=N'Daily Full Backup',
@enabled=1,
@notify_level_eventlog=0,
@notify_level_email=2,
@notify_level_page=2,
@delete_level=0,
@category_name=N'[Uncategorized (Local)]',
@owner_login_name=N'NISARG-PC\Nisarg',
@job_id = @jobId output
SELECT @jobId
go It will execute the job on my local workstation. Thus, we add it to the Job Server.
Execute the following query:
EXEC msdb.dbo.Sp_add_jobserver
@job_name=N'Daily Full Backup',
@server_name = N'NISARG-PC'
go The job step executes the backup database command. To configure the job step, use the following code:
USE [msdb]
go
EXEC msdb.dbo.Sp_add_jobstep
@job_name=N'Daily Full Backup',
@step_name=N'Generate Backup',
@step_id=1,
@cmdexec_success_code=0,
@on_success_action=1,
@on_fail_action=2,
@retry_attempts=0,
@retry_interval=0,
@os_run_priority=0,
@subsystem=N'TSQL',
@command=
N'Backup Database [AdventureWorks2017] to disk=''C:\Backups\AdventureWorks2017.bak'' with compression'
,
@database_name=N'master',
@flags=0
go The SQL Job will run daily at 1:00 AM. To configure the schedule, use the following code:
USE [msdb]
go
DECLARE @schedule_id INT
EXEC msdb.dbo.Sp_add_jobschedule
@job_name=N'Daily Full Backup',
@name=N'Run Backup At',
@enabled=1,
@freq_type=4,
@freq_interval=1,
@freq_subday_type=1,
@freq_subday_interval=0,
@freq_relative_interval=0,
@freq_recurrence_factor=1,
@active_start_date=20200918,
@active_end_date=99991231,
@active_start_time=10000,
@active_end_time=235959,
@schedule_id = @schedule_id output
SELECT @schedule_id
go The entire code of the job is as follows:
USE [msdb]
go
DECLARE @jobId BINARY(16)
EXEC msdb.dbo.Sp_add_job
@job_name=N'Daily Full Backup',
@enabled=1,
@notify_level_eventlog=0,
@notify_level_email=2,
@notify_level_page=2,
@delete_level=0,
@category_name=N'[Uncategorized (Local)]',
@owner_login_name=N'NISARG-PC\Nisarg',
@job_id = @jobId output
SELECT @jobId
go
EXEC msdb.dbo.Sp_add_jobserver
@job_name=N'Daily Full Backup',
@server_name = N'NISARG-PC'
go
USE [msdb]
go
EXEC msdb.dbo.Sp_add_jobstep
@job_name=N'Daily Full Backup',
@step_name=N'Generate Backup',
@step_id=1,
@cmdexec_success_code=0,
@on_success_action=1,
@on_fail_action=2,
@retry_attempts=0,
@retry_interval=0,
@os_run_priority=0,
@subsystem=N'TSQL',
@command=
N'Backup Database [AdventureWorks2017] to disk=''C:\Backups\AdventureWorks2017.bak'' with compression'
,
@database_name=N'master',
@flags=0
go
USE [msdb]
go
DECLARE @schedule_id INT
EXEC msdb.dbo.Sp_add_jobschedule
@job_name=N'Daily Full Backup',
@name=N'Run Backup At',
@enabled=1,
@freq_type=4,
@freq_interval=1,
@freq_subday_type=1,
@freq_subday_interval=0,
@freq_relative_interval=0,
@freq_recurrence_factor=1,
@active_start_date=20200918,
@active_end_date=99991231,
@active_start_time=10000,
@active_end_time=235959,
@schedule_id = @schedule_id output
SELECT @schedule_id
go We run the job manually for the demonstration first, by executing the code below:
use msdb
go
exec sp_start_job 'Daily Full Backup'You can view the status of the job by running the following query:
SELECT NAME
AS [Job Name],
CONVERT(VARCHAR, Dateadd(s, ( run_time / 10000 ) * 60 * 60
+ ( ( run_time - ( run_time / 10000 ) *
10000 ) /
100 ) * 60
+ ( run_time - ( run_time / 100 ) * 100
), CONVERT(DATETIME, Rtrim(run_date), 113)), 100)
AS
[Job Executed Date and Time],
CASE
WHEN enabled = 1 THEN 'Enabled'
ELSE 'Disabled'
END
[Job Status],
CASE
WHEN JobHistory.run_status = 0 THEN 'Failed'
WHEN JobHistory.run_status = 1 THEN 'Succeeded'
WHEN JobHistory.run_status = 2 THEN 'Retry'
WHEN JobHistory.run_status = 3 THEN 'Cancelled'
ELSE 'Unknown'
END
[Job Outcome]
FROM sysjobhistory JobHistory
JOIN sysjobs Jobs
ON JobHistory.job_id = Jobs.job_id
WHERE NAME = 'Daily Full Backup' Output:
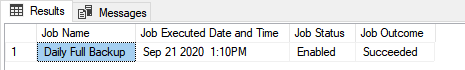
To view the backup file, Open the C:\Backups location:
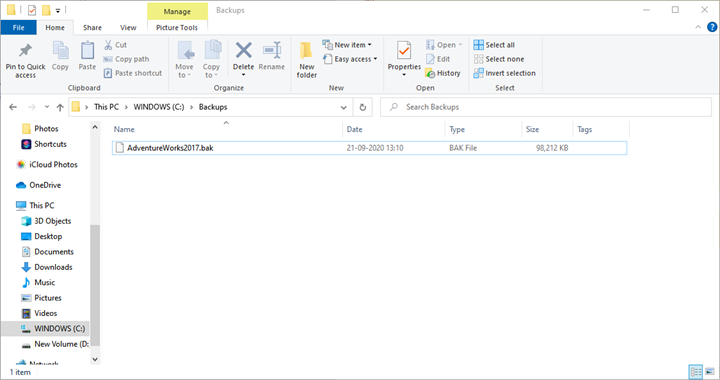
As you can see, the backup file has been created.
Tags: automation, database administration, sql server, t-sql queries Last modified: September 20, 2021